Ransomware attacks have risen in the last year, and the repercussions are widespread. In the SOPHOS State of Ransomware 2022 survey, 66% of respondents reported that they were hit by ransomware in the previous year – a 78% increase from the year before. In nearly two-thirds of these incidents, attackers encrypted data.
Overall, the average cost to remediate a ransomware attack was a business-crippling $1.4 million. Furthermore, 90% of victims said a ransomware attack impacted their ability to operate, while 86% of private sector organizations said it caused them to lose business/revenue.
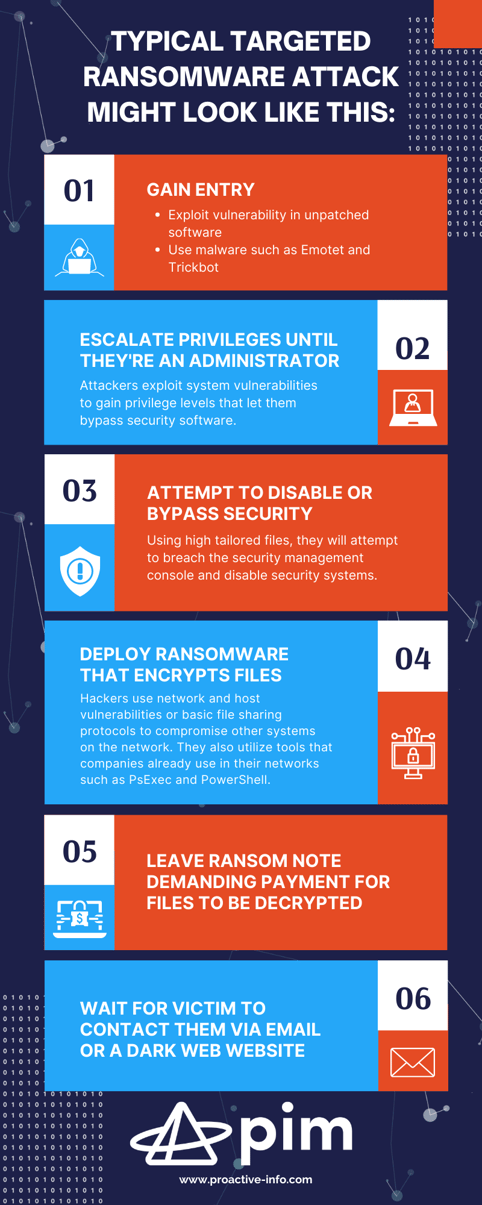
.png?width=2000&height=800&name=typical%20targeted%20ransomware%20attack%20(1).png)
Best Practices to Protect Against Ransomware
Staying secure against ransomware requires more than just having the latest security solutions. Good IT security practices, including regular employee training, are essential. Make sure you’re following these nine best practices.
1. Patch early and often
The exploitation of unpatched vulnerabilities was the root cause for almost half (47%) of cyber incidents investigated by Sophos in 2021. Malware often relies on security bugs in popular applications. The earlier you patch your endpoints, servers, mobile devices, and applications, the fewer holes that cybercriminals can exploit.
2. Back up regularly and keep a recent backup copy offline and offsite
In our State of Ransomware 2022 survey, 73% of IT managers whose data was encrypted were able to restore it using backups. Encrypt your backup data and keep it offline and offsite so you won’t have to worry about cloud backups or storage devices falling into the wrong hands. Moreover, restore data from backups regularly.
3. Enable file extensions
The default Windows setting is to hide file extensions, meaning you must rely on file thumbnails to identify them. Enable extensions to make it easier to spot JavaScript (JS) files and other file types that aren’t commonly sent to you and your users.
4. Open JS files in Notepad
Opening a JS file in Notepad blocks it from running any malicious scripts and allows you to examine the file’s contents.
5. Don’t enable macros in document attachments received via email
Microsoft deliberately turned off auto-execution of macros by default many years ago as a security measure. Many infections rely on persuading you to turn macros back on — DON’T DO IT!
6. Be cautious about unsolicited attachments
Cybercriminals often rely on an ages-old dilemma: knowing that you shouldn’t open a document until you are sure it’s legitimate but not being able to tell if it’s malicious until you open it. When in doubt, leave it out.
7. Monitor administrator rights
Constantly review local and domain admin rights. Know who has them and remove those who don’t need them. Don’t stay logged in as an administrator any longer than necessary. And avoid browsing, opening documents, or performing other regular work activities while you have admin rights.
8. Regulate internal and external network access
Don’t leave network ports exposed. Lock down your organization’s RDP access and other remote management protocols. Also, use two-factor authentication and ensure remote users authenticate against a VPN.

9. Use strong passwords
It sounds trivial, but it isn’t. A weak and predictable password can give hackers access to your entire network in seconds. We recommend making passwords unique, having them consist of at least 12 characters, using a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, and adding a random punctuation Ju5t.LiKETh1s!
Best Practices for Your Endpoint Security Solution
1. Use the default policy recommendations and ensure all features are enables
- Enable tamper protection
- Enable forensic logging (ideally to the cloud)
2. Regularly review your exclusions
- Exclusions prevent trustworthy directories and file types from being scanned
- A growing list of excluded directories and file types can impact many people across a network
3. Enable MFA
4. Ensure every endpoint is protected and up to date
- Check devices regularly
- An incorrectly functioning device could be vulnerable to attacks
5. Maintain good IT hygiene
- Mitigates cybersecurity risk
- An incorrectly functioning device could be vulnerable to attacks
6. Proactively hunt for active adversaries across your network
- Deploy deception technology like Dragnet
- Make use of EDR/XDR if you have them
- Consider utilizing MDR services for 24/7 threat