Penetration Testing for the Die Hard Fan
Penetration testing, commonly referred to as pen testing, is a proactive cybersecurity approach...
Businesses and home users alike are under threat from increasingly aggressive and brutal ransomware attacks. Loss of access to critical files, followed by a demand for payment can cause massive disruption.
But what does a typical attack look like? And what security solutions should be in place to give the best possible defense?
This post highlights the commonly used techniques to deliver ransomware and outlines some security recommendations to help you stay secure.
Ransomware attacks are showing no signs of slowing down and hackers are getting ever craftier at getting round cybersecurity defenses.
In a recent survey of 5,400 companies across 30 countries, 37% said that they had fallen victim to a ransomware attack in 2020. It’s a huge issue – and we are all part of the solution. 51% of respondents in the United States said they experienced ransomware. Clearly, ransomware is one of the most widespread and damaging threats that internet users face. It makes the news nearly every single day in shape or form. Cyber criminals are getting smarter and are evolving attacks constantly meaning ransomware isn’t going away anytime soon.
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that cybercriminals use to extort money from their victims.
First hackers, using several different methods, attempt to gain access to your computer and ultimately, your personal files and data. Once they have achieved this, they install the ransomware.
The ransomware then executes and encrypts your valuable files such as Word documents, Excel spreadsheets and sensitive data so that they can’t be used. Hackers then demand a ransom payment in return for access to your files.
Attackers can get into your system in multiple ways.
Anti-ransomware technology has a key role in stopping it. But when it comes to IT security everyone has a part to play! Educating yourself is critical in spotting bogus emails and compromised websites both of which could give hackers an easy way into your network. To help you identify and avoid ransomware we’ve put together a few quick tips that apply whether you’re in the office or at home.
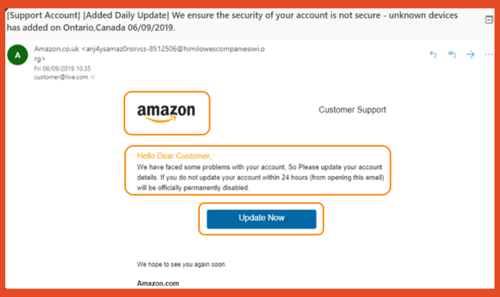
Well, before you can spot a phishing email, it’s important to understand what phishing is.
Phishing is any type of attempt to trick you into doing something to benefit the crooks, usually through an email.
The three most spoofed brands that hackers attempt to mimic in emails are Apple, Amazon, and Microsoft. Their global coverage and high brand recognition makes them ideal targets for cybercriminals in their phishing attacks.
To the untrained eye, a mass phishing email can easily go undetected and provide hackers with swift access to your computer.
Watch out for file types that you aren’t familiar with or use in your day-to-day work. They are often disguised as other file types to fool you into clicking on them. If you aren’t sure about it, check with pim.
P: Promises—Does it promise unbelievable things?
H: Harassment—Is it harassing you or pressuring you to get a reply?
I: Instincts—Does this “feel” wrong?
S: Sense of Urgency—Is there a time crunch? Is it insisting you act now or else?
H: Hit delete. Don’t click or engage. Just delete!
If in doubt, report it to pim and hit delete to make everyone else in the company aware of the phish!
.png?width=300&name=Screenshot%20(1969).png)
The web is a fantastic place to find memes, but it’s also one of the keyways hackers are able to access your computer to install ransomware.
Make sure that links go to where you think they do. Often crooks will disguise a website address to make it look authentic.
They also use a trick known as masking. Masking is where the link looks legitimate but when you click on it, you’re taken somewhere completely different. However, if you hover over a link before you click on it you can see where it really goes.
A weak password is an easy road in for a hacker to access your online accounts.

We also recommend using a unique password for each online account that you have. We do appreciate that this entails problems of its own however, if a hacker gets a hold of a password that is used on multiple accounts, then a hacker now has access to several of your accounts.
We recommend using a password manager to help with having to remember eleventy thousand unique passwords for multiple accounts.
Furthermore, should you ever change your password, the manager will recognize this and amend its database automatically.
You may feel a bit wary having all your passwords stored in one central place, but any password manager worth its salt uses heavy-duty encryption to keep your information safe. In addition, many offer two factor authentication (2FA), adding another layer of security.
Penetration testing, commonly referred to as pen testing, is a proactive cybersecurity approach...
Penetration testing, also known as pentesting, is a process of simulating real-world cyberattacks...
